GIS is a key tool for understanding complex territories and addressing environmental, social, and economic challenges. Furthermore, the use of spatial data allows for integrated readings of phenomena and more informed decisions. This is the context for gisAction Solutions, designed to integrate GIS into analysis, planning, monitoring, and decision support processes.
gisAction Solutions combine GIS systems, territorial databases, spatial analysis tools, and web platforms. In this way, large amounts of heterogeneous data become structured and easily readable information. Interactive maps and thematic dashboards facilitate data exploration. In addition, decision support systems help identify critical issues and evaluate scenarios. Particular attention is paid to the data lifecycle. First collection, then validation, then analysis, and finally dissemination. This ensures consistency, updating, and reliability.
Areas of application for gisAction solutions
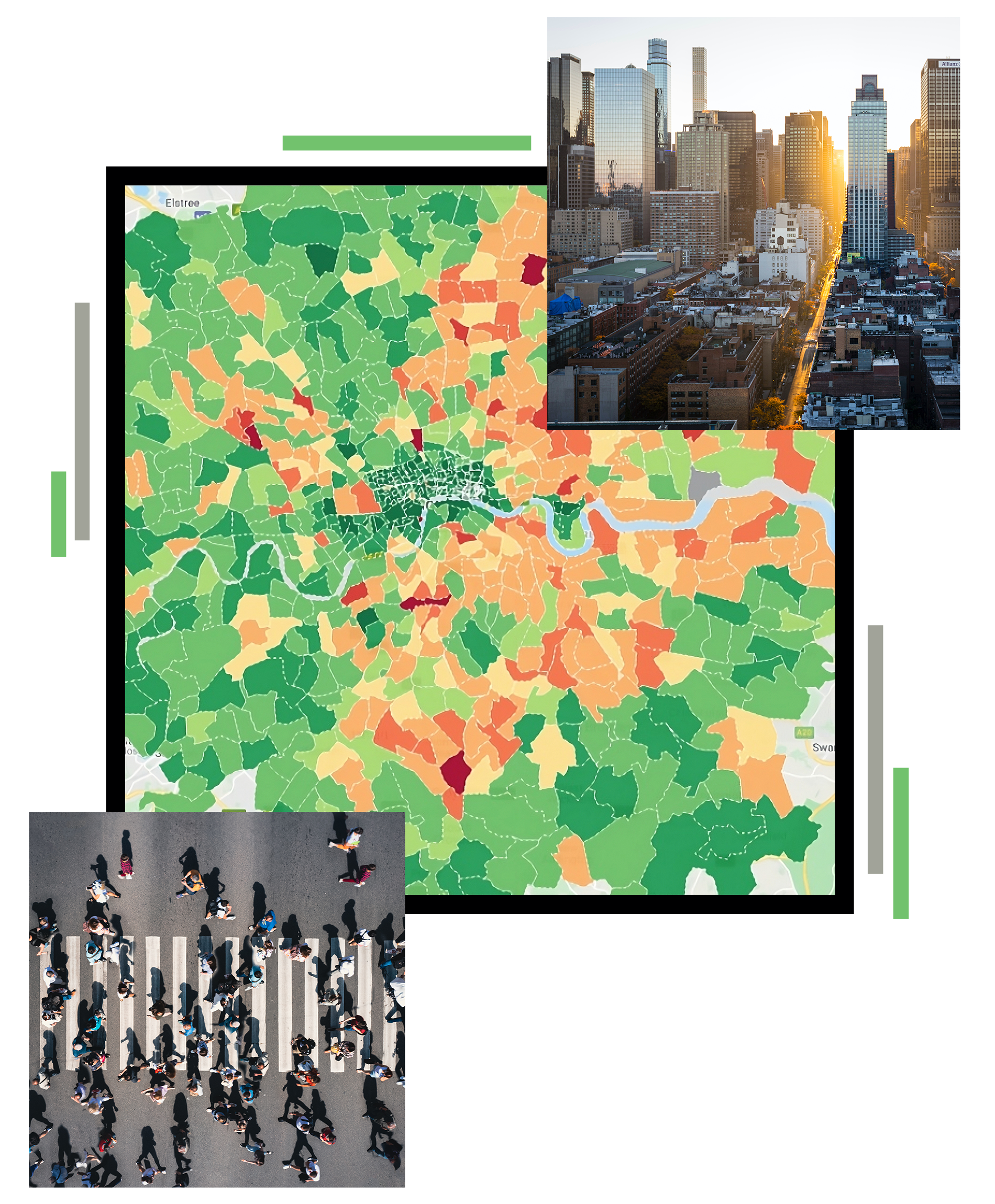

GIS solutions for national statistics: data analysis and dissemination with geodatabases, real-time monitoring, and interactive maps.
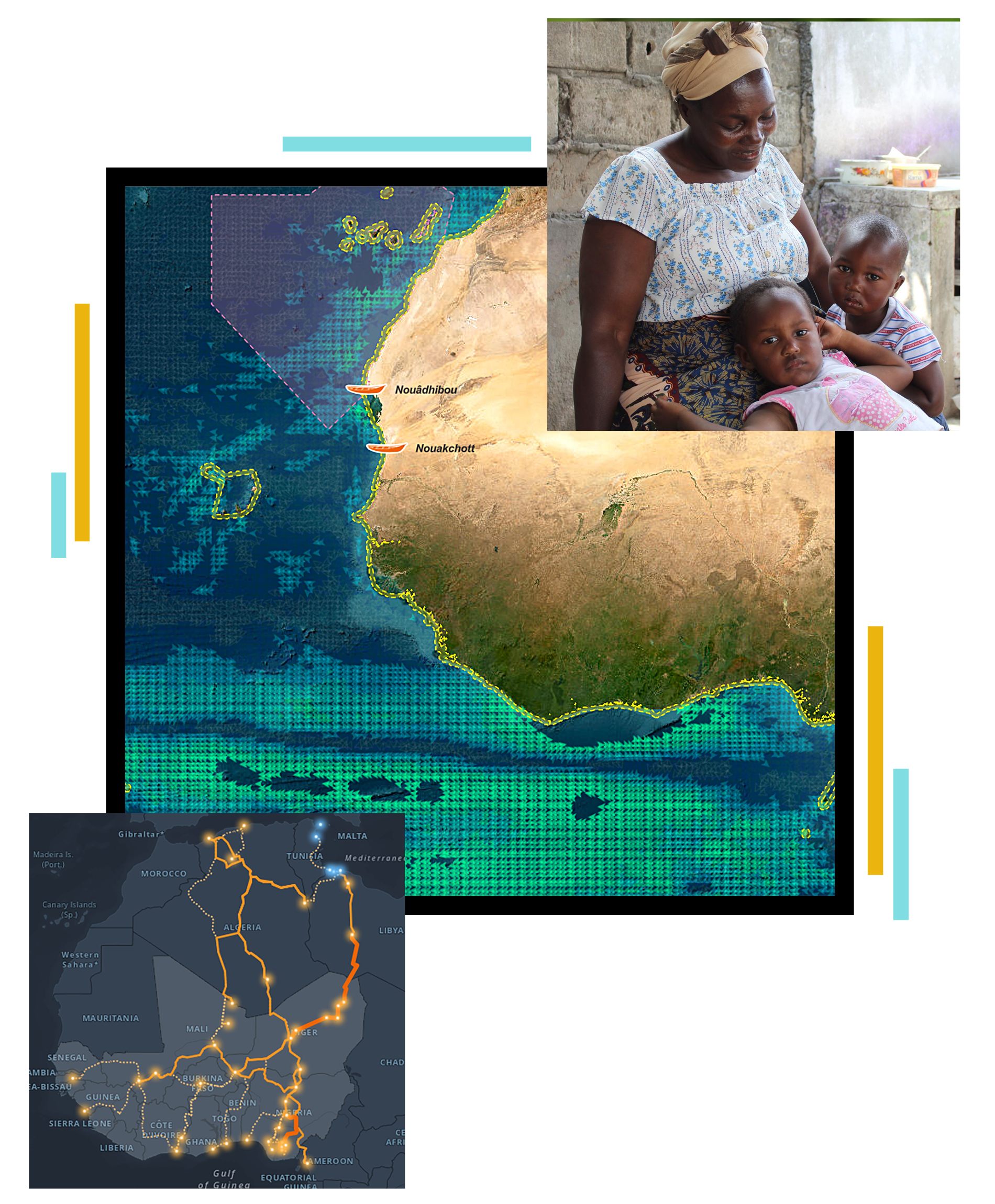

GIS for International Cooperation and MEAALs: planning, monitoring, impact evaluation, and communication of results.
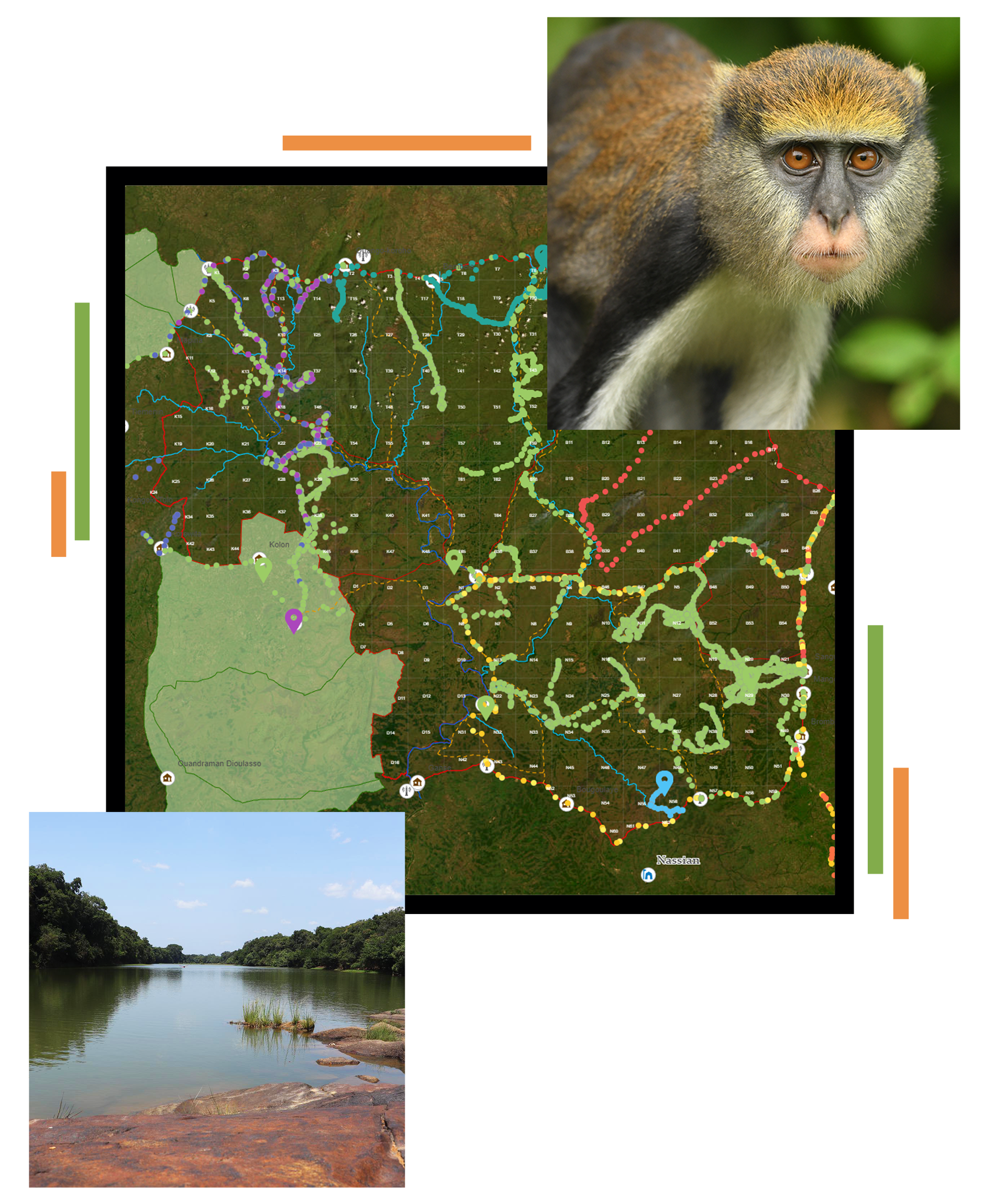

GIS for Conservation: park surveillance, biomonitoring, operational safety, and decision support for environmental protection.
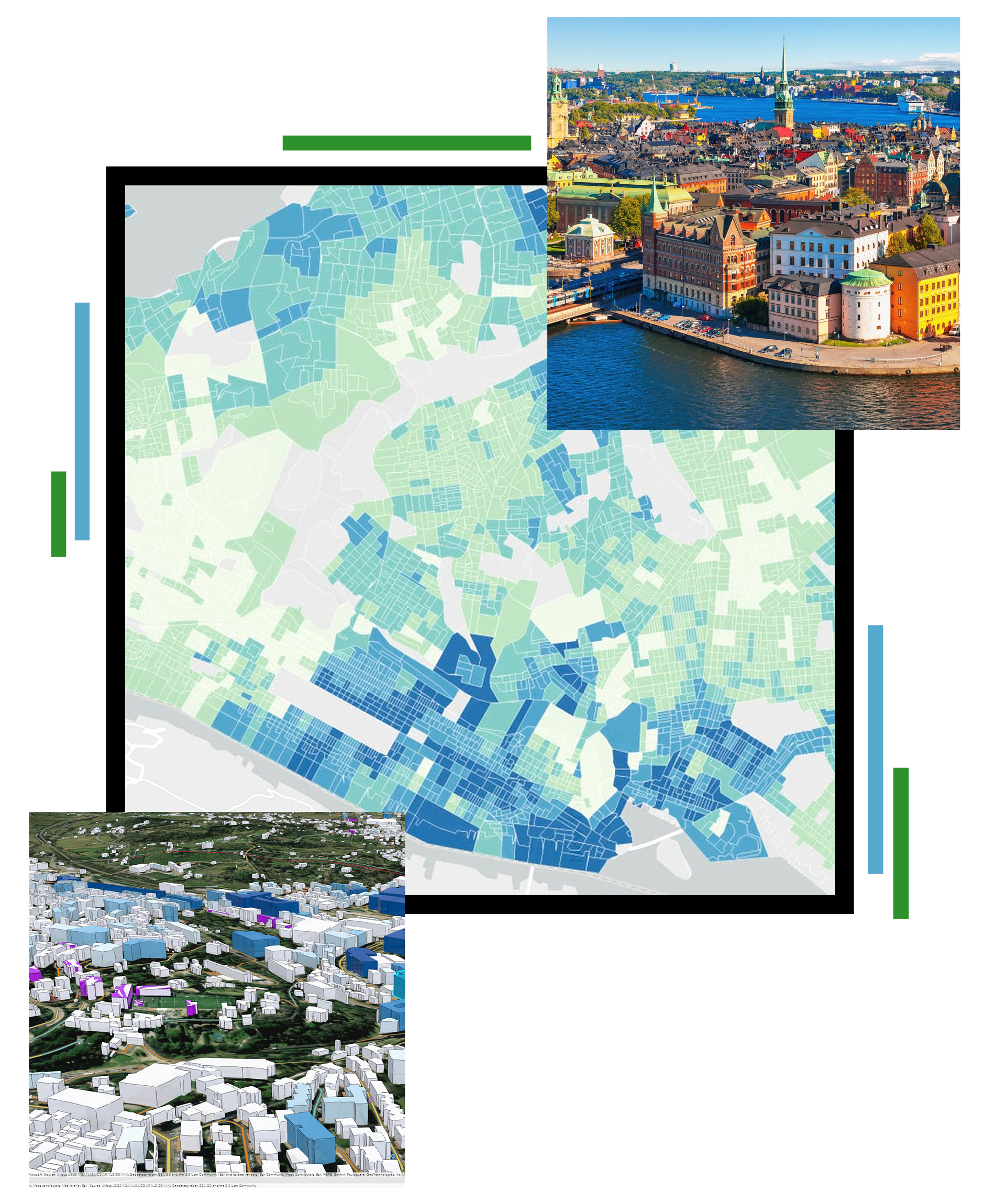
GIS Solutions for Urban Regeneration: territorial analysis, intervention monitoring, and sustainable urban development.

GIS for Cultural Heritage: mapping, 3D models, enhancement, accessibility, and protection of cultural assets.
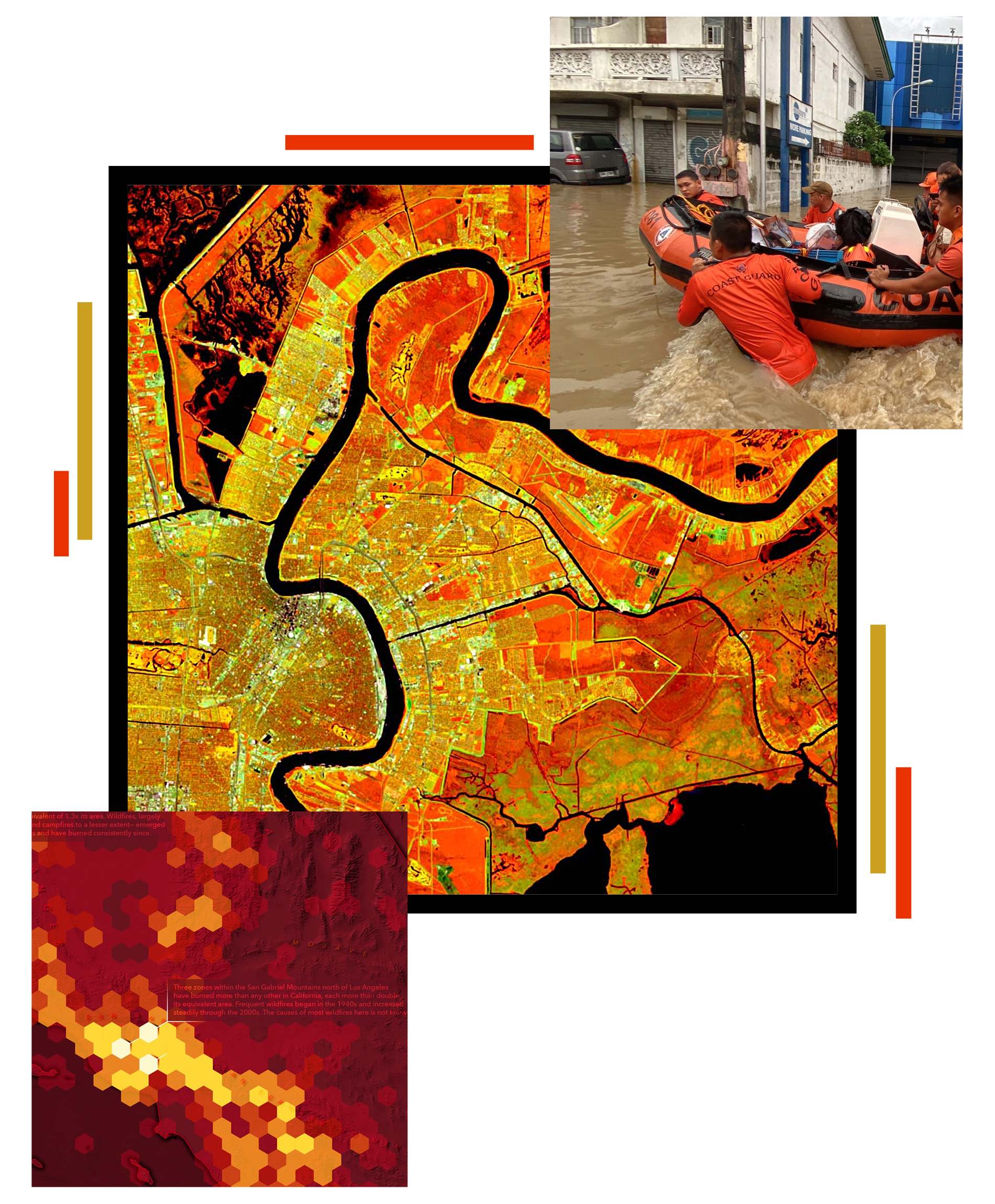
GIS for climate and disaster risk reduction: climate analysis, risk mapping, emergency planning, and management.

GIS for the Data Value Chain – management, analysis, visualization, and value creation of geospatial data in decision-making processes.
In each area, gisAction solutions integrate territorial, environmental, social, and economic data. As a result, they offer a unified view of phenomena. They also promote more effective planning and greater risk awareness. At the same time, they support the assessment of the impact of policies and interventions. Finally, they contribute to long-term sustainability. GIS thus becomes a shared operational tool. For this reason, it facilitates coordination between different actors and the development of strategies based on knowledge of the territory. Finally, this approach promotes transparency, institutional collaboration, system interoperability, and efficient information management at the local and regional levels to support public policies based on reliable shared territorial data.
